Interesting Facts about the Circulatory System
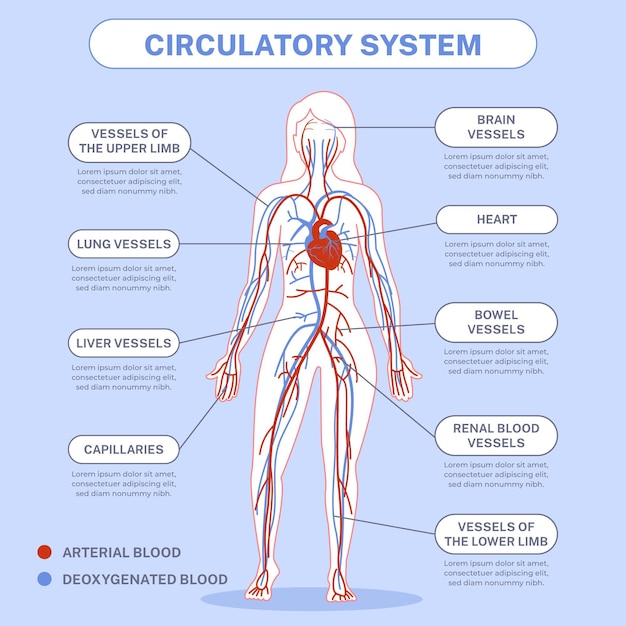
The circulatory system is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell in our body.
Did you know that the heart beats about 100,000 times a day?
The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
The heart is about the same size as your fist.
The circulatory system is like a highway network, transportation nutrients and oxygen to where they are needed.
Without a properly functioning circulatory system, our body would not be able to survive.
The heart pumps approximately 2,000 gallons of blood every day.
The capillaries in our body can stretch up to 25,000 kilometers if placed end to end.
Blood vessels come in different sizes, ranging from thin capillaries to large arteries and veins.
The red color of blood comes from the iron in red blood cells.
The circulatory system works together with the respiratory system to ensure a constant supply of oxygen.
Blood carries waste and carbon dioxide away from the cells to be eliminated from the body.
The circulatory system helps to regulate body temperature by distributing heat throughout the body.
Did you know that blood actually carries hormones that help to regulate important processes in our bodies?
The human heart starts beating around 4 weeks after conception.
Blood travels through your body in less than one minute.
Interesting Facts about the Circulatory System part 2
The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
The circulatory system of a blue whale can hold over 1,000 gallons of blood.
Your heart creates enough energy to drive a truck for 32 kilometers every day.
The clotting ability of blood helps to prevent excessive bleeding when we get injured.
The circulatory system can be affected by factors such as diet, exercise, and genetics.
Blood pressure is a measure of the force of blood against the walls of blood vessels.
The circulatory system ensures that all organs and tissues receive a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients.
The heart does not only work during the day; it continues to pump blood even while we sleep.
The circulatory system plays a crucial role in the immune response, helping to fight off infections and diseases.
Blood is living tissue, carrying out essential functions in our bodies.
The circulatory system of a horse is around eight times larger than that of a human.
Maintaining a healthy circulatory system requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding habits like smoking.
Blood thinners can help to prevent blood clots from forming and causing health problems.
Your heart rate can increase during exercise to ensure that enough oxygen-rich blood is supplied to muscles.
The heart muscle is so strong that it can keep pumping blood even if you cut it out of the body.
High blood pressure can put a strain on the heart and increase the risk of heart disease.
The circulatory system can sometimes experience problems like blockages, leading to heart attacks or strokes.
Did you know that giraffes have a particularly strong circulatory system to pump blood all the way up to their heads?
The circulatory system works silently behind the scenes, ensuring that all our organs and tissues receive what they need to function properly.
Runners often have a lower resting heart rate because their hearts are more efficient at pumping blood.
Blood flows through the smallest vessels in our body at a speed of only one centimeter per second.
When you blush, it’s not just your face turning red; blood vessels throughout your body expand, causing a reddish hue.
The oxygenated blood in our body is usually bright red, while deoxygenated blood appears more blue.
Blood cells are constantly being produced and destroyed in our body to maintain a healthy balance.
The circulatory system helps to distribute antibodies and immune cells that help us fight off infections.
If you tied all the blood vessels in your body end-to-end, they would stretch over 60,000 miles.
The circulatory system can adapt to changes, such as increasing blood flow to muscles during exercise.
Our heart has its own electrical system that keeps it beating in a coordinated rhythm.

