Interesting Facts About Plant Cells
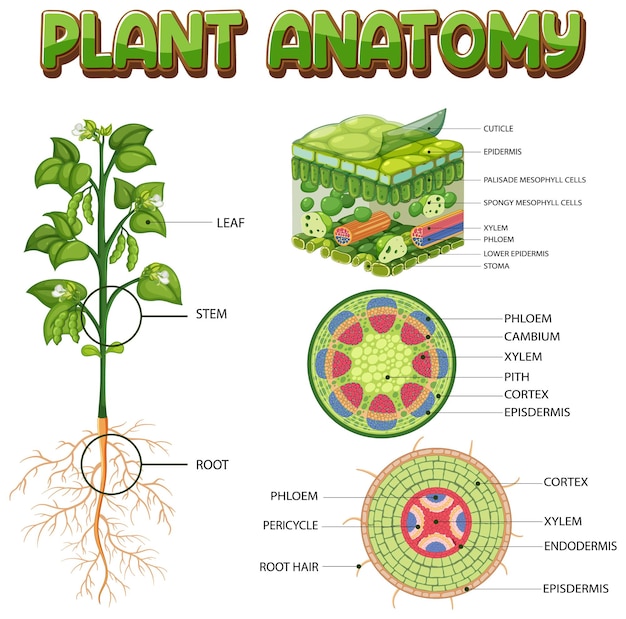
Plant cells are the building blocks of all plant life.
The plant cell is the basic unit of structure and function in plants.
Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose.
Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole that helps maintain turgor pressure and store water and nutrients.
Plant cells have a nucleus that stores genetic information and controls cellular functions.
The mitochondria in plant cells produce energy through cellular respiration.
Plant cells communicate with each other through plasmodesmata, small channels that allow for the exchange of molecules and information.
Plant cells can differentiate into various specialized cell types, such as root cells, leaf cells, and stem cells.
Plant cells are capable of cell division, allowing for growth and repair.
Plant cells have a diverse range of organelles, each with specific functions.
Plant cells can adapt to environmental changes to ensure their survival.
Plant cells contain starch granules, which are used for energy storage.
The cell membrane in plant cells regulates the entry and exit of molecules.
Plant cells have a unique organelle called the peroxisome, which helps break down toxic substances.
Plant cells have a rigid shape due to their cell wall, providing structural support.
Plant cells can reproduce sexually or asexually, depending on the species.
Interesting Facts About Plant Cells part 2
Plant cells play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis.
The size and shape of plant cells can vary depending on their function within the plant.
Plant cells can undergo programmed cell death, known as apoptosis, to remove damaged or unnecessary cells.
Plant cells have mechanisms to defend against pathogens and pests.
Plant cells contain multiple membrane-bound compartments, allowing for compartmentalization of different cellular processes.
Plant cells are capable of repairing and regenerating damaged tissue.
Plant cells have a cytoskeleton that provides structural support and helps maintain cell shape.
Plant cells have a specialized endoplasmic reticulum called the rough endoplasmic reticulum, involved in protein synthesis.
Plant cells have a specialized organelle called the Golgi apparatus that modifies and packages proteins for transport.
Plant cells can communicate with neighboring cells through chemical signals.
Plant cells have a complex network of microtubules and microfilaments, allowing for intracellular transport.
Plant cells have a unique phragmoplast structure that forms during cell division and helps build new cell walls.
Plant cells have mechanisms to sense and respond to environmental cues, such as light and gravity.
Plant cells have a cytoplasm that contains various organelles and serves as a site for cellular metabolism.
Plant cells have unique plasmodesmata connections that enable the exchange of nutrients and signals between neighboring cells.
Plant cells can synthesize complex carbohydrates, such as cellulose and pectin, for cell wall formation.
Plant cells can differentiate into specialized tissues, such as xylem and phloem, for transport of water, nutrients, and sugars.
Plant cells can synthesize secondary metabolites, such as alkaloids and flavonoids, with various medicinal and ecological functions.
Plant cells have a unique system called the vacuolar trafficking pathway to transport molecules within the cell.
Plant cells have a specialized organelle called the peroxisome, involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification processes.
Plant cells have a unique lipid composition in their membranes, adapting to withstand different environmental conditions.
Plant cells can undergo cellular elongation to facilitate growth and development.
Plant cells have a variety of sensors that allow them to respond to changes in temperature, light intensity, and nutrient availability.
Plant cells have a unique reproductive structure called the pollen grain, which carries male gametes for fertilization.
Plant cells have a wide range of organelles involved in photosynthesis, such as the thylakoids and chloroplast envelope.
Plant cells have the ability to repair DNA damage, ensuring genetic stability.
Plant cells have a unique mechanism of programmed cell death called autophagy, which eliminates damaged organelles and recycles their components.
Plant cells have the ability to regenerate entire plants through a process called totipotency.

