Earthquake Fun Facts
Earthquakes can occur at any time, so it’s important to always be prepared.
The largest recorded earthquake in history was the Great Chilean earthquake of 1960, with a magnitude of 9.5.
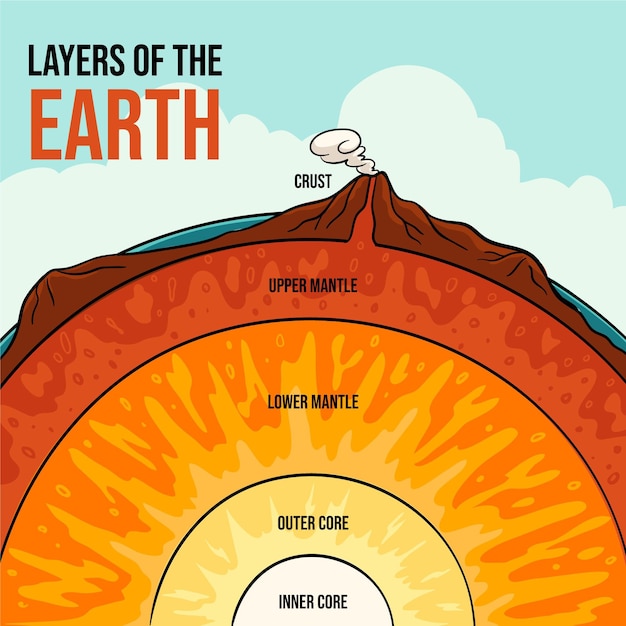
Earthquakes often occur along fault lines, where tectonic plates meet.
Some animals can sense earthquakes before they happen, giving people a warning sign.
Earthquakes can cause landslides and avalanches in mountainous regions.
The energy released during an earthquake is equivalent to the explosion of multiple atomic bombs.
Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale, which indicates the magnitude of the seismic activity.
The first seismograph, a device used to measure earthquakes, was invented by Chinese scientist Zhang Heng in 132 AD.
Earthquakes can trigger other natural disasters, such as tsunamis and volcanic eruptions.
The Ring of Fire, a major area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean, is known for its frequent earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The San Andreas Fault in California is one of the most well-known and active fault lines in the world.
The city of Tokyo, Japan, experiences thousands of small earthquakes every year.
Earthquakes can cause structural damage to buildings and infrastructure, leading to potential risks for human safety.
Earthquakes are a result of the Earth’s natural processes of plate tectonics and continental drift.
The impact of an earthquake can be felt hundreds of miles away from its epicenter.
Earthquake Fun Facts part 2
Scientists use seismographs and GPS systems to track and study earthquakes.
The term aftershock refers to smaller earthquakes that follow a major earthquake.
Some regions, such as Iceland and New Zealand, have a higher frequency of earthquakes due to their proximity to tectonic plate boundaries.
Earthquakes occur on other planets and moons as well, indicating geological activity beyond Earth.
You can’t predict exactly when and where an earthquake will occur, but scientists are working on improving early warning systems.
Earthquakes can alter the Earth’s rotation and change the length of a day.
The 1906 San Francisco earthquake and subsequent fires destroyed much of the city and led to significant changes in urban planning and building codes.
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan caused the meltdown of a nuclear power plant, leading to serious environmental and health hazards.
Some people believe that certain geological formations, such as ley lines, can influence earthquake occurrences.
The Great Hanshin earthquake in Kobe, Japan, in 1995 resulted in over 6,000 deaths and massive infrastructure damage.
During an earthquake, it is essential to drop, cover, and hold on to protect yourself from falling objects and debris.
Earthquakes can create temporary changes in groundwater levels and even cause new springs to emerge.
The frequency of earthquakes varies greatly, with some areas experiencing multiple small tremors every day, while others may have years between significant quakes.
The 1906 San Francisco earthquake inspired the development of earthquake-resistant building designs and construction techniques.
The study of earthquakes and their effects is known as seismology.
Earthquakes can cause significant economic damage due to disrupted infrastructure and business activities.
Some cities, like Los Angeles, have building codes that require structures to be designed to withstand seismic activity.
The ocean floor is constantly experiencing seismic activity due to the shifting of tectonic plates.
The deadliest earthquake ever recorded occurred in 1556 in Shaanxi, China, with an estimated death toll of 830,000.
Earthquakes often create unique geological formations, such as fault scarps and grabens.
The 1906 San Francisco earthquake had a magnitude of around 7.8 and lasted for approximately 45-60 seconds.
The Richter scale is logarithmic, meaning that each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in seismic energy.
Earthquakes can trigger the release of methane gas from underground deposits, contributing to climate change.
The 1964 Good Friday earthquake in Alaska was the second-largest earthquake ever recorded, with a magnitude of 9.2.
Seismologists use different types of waves, such as P-waves and S-waves, to understand the characteristics and path of seismic energy.
Earthquakes in densely populated areas often have more severe consequences due to the concentration of people and infrastructure.
Many countries have established earthquake early warning systems that provide alerts before the shaking reaches densely populated areas.
Earthquakes can induce soil liquefaction, which causes the ground to behave like a liquid and leads to building collapse.
The Great Lisbon earthquake of 1755 and its resulting tsunami had a profound impact on the architecture and urban planning of European cities.
Despite the destructive power of earthquakes, they are also a reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature and the constant change happening beneath our feet.

